Brands
What is Technical SEO and How Does It Impact Content Performance?
Most of us content marketers consider the content side of SEO at the very beginning of any project; we’ve become adept at marrying ideas with the right keywords, information, and heading structures so that the message and SEO go together harmoniously—like peanut butter and jelly.
Technical SEO, on the other hand, might not be as fully understood. We know it’s important, but it’s often left up to SEO or IT teams, who may (or may not) have a comprehensive understanding of the broader marketing strategy. But that doesn’t mean content marketers can’t grasp and implement the basics of technical SEO to complement a great marketing strategy.
Why Does Technical SEO Matter to Content Marketers?
As you likely already know, SEO is key to online success. In fact, nearly 50% of shoppers today begin their research with Google—so ranking on the first page of search engine results pages (SERPs) can offer serious opportunities to reach your ideal customers.
That’s where technical SEO comes in. When you optimize your website’s tech aspects, you make it easier for search engines like Google to find, crawl, and rank it.
These behind-the-scenes tweaks might not be flashy, but creating a faster, more mobile- and crawler-friendly website can help your page rank closer to the top of the search results. Even if you have the best content in the world, if no web traffic stops by, you might as well be writing on paper and then tucking it away in a desk drawer.
So, if you want more eyeballs on your site, you need to do two things — create quality content and follow these technical SEO recommendations — to set your site apart from competitors.
Get Cozy With Google Search Console
First, take some time to get comfortable with using Google Search Console. It offers insights into your website’s overall performance—from the keywords it’s ranking for to how to fix performance issues and how it stacks up against competitors.
It’s especially handy for SEO recommendations related to your site’s Core Web Vitals, a report that uses field data—aka data from real-world users—to gauge the performance of various URLs on your site.
The report has much to do with site and page speed or how fast a page loads. According to Google, when a site meets the Core Web Vitals threshold, users are 24% less likely to abandon it before it loads. (After all, it’s not 1998 – we’ve gotten used to our internet moving lightning fast.) Following SEO recommendations to achieve better Core Web Vitals can also lead to:
- Increased page views per session
- Longer sessions per visit
- Lower bounce rates
A faster website means a better user experience. Combine a fast site with useful, interesting content, and you can improve consumer sentiments surrounding your brand, keep visitors on your website longer, and, ultimately, boost sales or conversions.
Embrace Structured Data and Schema Markups
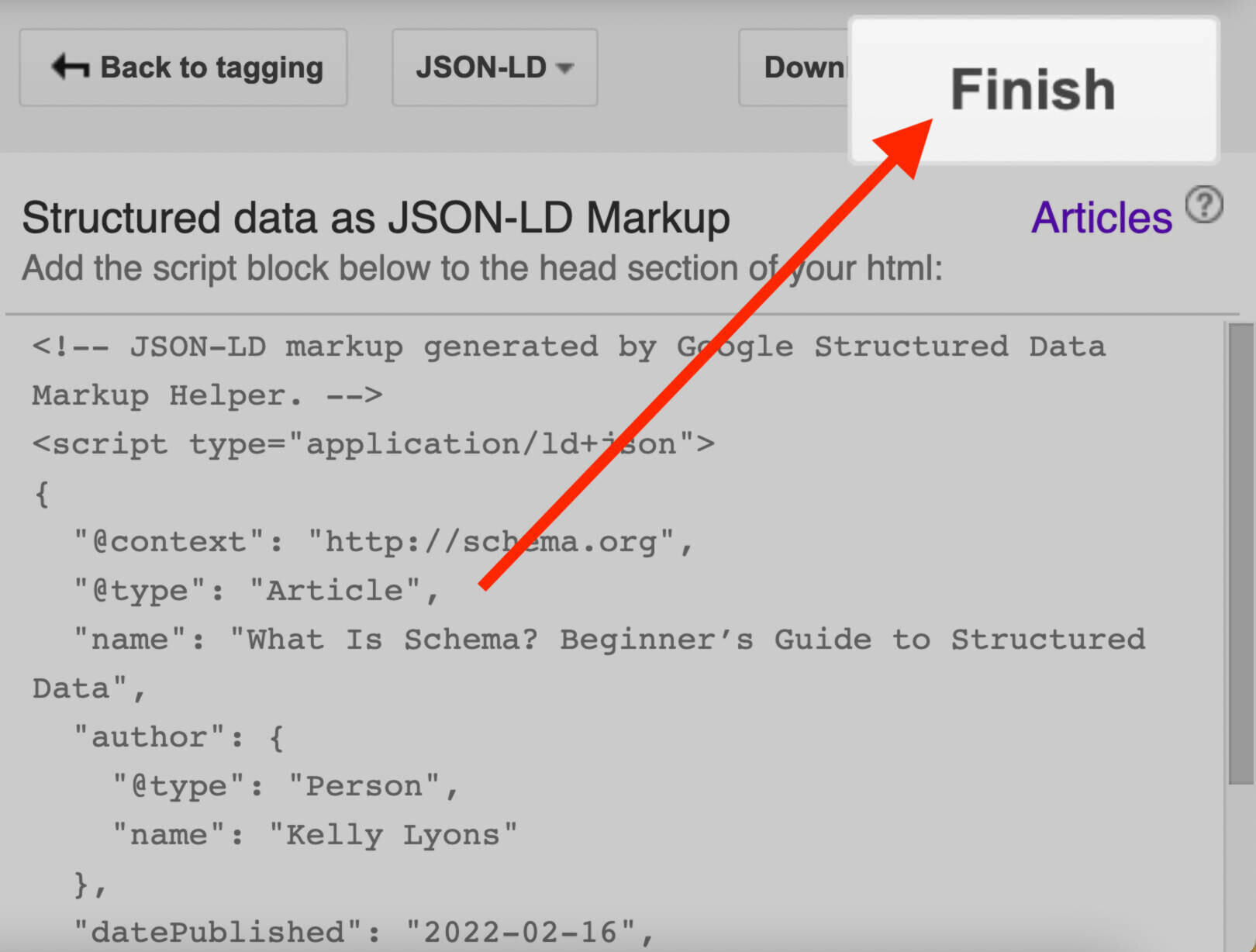
Here’s where things get, well, a bit technical. However, as a marketing professional (who may have a limited understanding of coding), you can still use structured data and schema markups to your advantage.
Structured data uses a language called schema markups to explain the information on a webpage so search engines can easily understand it. Schema helps search engines crawl your website; it explains to Google and the other search engines what they can expect to find in the content that follows the code.
Basically, structured data is like adding labels to different parts of a webpage to tell search engines what each piece of information is about. For example, in a recipe, schema markups can tell Google which section contains the list of ingredients, which part contains the cooking time, and so on. Helpful, right?
By using structured data and schema markups, we can give search engines more context about a website’s content (try saying that 10 times fast). This helps search engines display richer search results, improving the user experience and making it easier for people to find what they’re looking for online.
People often forget useful SEO recommendations like using Schema markups. Fortunately, it’s easier than ever to use structured data to help your website get found by search engines.
Schema Made Simple
Even though Schema has been around for a while, it’s still highly relevant to SEO recommendations. One experiment found that twice as many sites with schema markups gained rankings in search engine results.
Check out Schema.org, where you can find a list of coding terms that can help your SEO; it was founded in 2011 by Google, Microsoft, and Yahoo to provide a common language that leads to better and more consistent search results, and it has all kinds of schema types available for you to browse.
Pro tip: You can easily add schema markups to your website using WordPress plugins like Schema Pro. These plugins automate markups and can also create Custom Fields.
Know Your Link Strategy
A strong internal link-building strategy is one of the basics of a good SEO strategy. When creating a new piece of content, think about other content on your site that is valuable, relevant, and related to the piece you’re writing to include as a hyperlink. For example, if you’re writing about savings accounts and mention compound interest, linking to an article on the topic would help your readers understand the bigger picture.
Many SEO recommendations suggest five to 10 internal links for every 2,000 words of content, which is roughly one link for every 200 words.
You can add links to your higher-traffic pages to support them or lower-traffic pages to boost them. But don’t overdo it! Adding too many links could distract, overwhelm or divert your reader from reaching the CTA.
It’s also worth it to run a check every once in a while to make sure you’re not linking to URLs that have been changed, deleted or moved. These “dead links” do nothing to help your search ranking and decrease readability.
Understanding External Links/Backlinks
External links/backlinks are another matter altogether. They come in two forms:
- Outbound links, which go from your web page to an external authoritative page
- Inbound links, which go from another authoritative site to your content
Let’s first talk about the ones we can control: Outbound links.
Outbound Links
If you’re writing about a topic, you can add links to pages that aren’t part of your site. These outbound links give readers more information on the topic from an authoritative source, like a government site or scientific study. When you’re linking to other sites, choose ones that:
- Don’t compete with yours
- Have credibility as a primary or authoritative source
- Are trustworthy
If the site doesn’t meet these requirements, but you still want to link to it – for instance, in the case of a sponsorship—add a “nofollow” link. Google won’t acknowledge that you linked to the page, but your readers can find it with a click.
Inbound links
Just as you want to link to authoritative sites, you want other sites to link to your content as a helpful resource, too. Google frowns upon link trading, buying links, or other ways of securing links that do not happen organically. It considers them “Link spam”; you should mark them with “nofollow” or risk being penalized. So keep an eye on your backlinks (using your trusty Google Search console or other tool) to make sure you’re in line with Google’s rules.
Instead, you can offer to post guest blogs on relevant sites or ask partners or influencers to link to you. If another site references your content—such as the results of a survey or study—you can reach out and ask if they can add a backlink. Similarly, if someone posts a positive review of your brand on their website, ask them for a link.
Effective link-building is a lot of work, but it can offer a valuable boost in rankings.
Link Disavowal
If Google sends you a scary-looking manual action for “unnatural links,” you can log into Google Search Console and browse the list of sites that link to you for the offending links. You can then request that Google disregard those links. There’s no guarantee that Google will do what you ask, and this may impact your search rankings—for better or worse—but it’s better than having bad links slowly tank your rankings.
Put in the Time to Become a Technical SEO Pro
Following technical SEO recommendations requires patience, attention to detail, and determination—especially if you have to level up your knowledge along the way. But just like any other skill, mastering it adds value and insight to your content.
Don’t Skip the Technical SEO Audit
Most people’s shoulders tense up with the mention of the word “audit,” but in this case, it just means assessing the technical SEO methods your site already uses, how well it uses them, and what you could implement to improve it. If you feel like you might need some help along the way, there are always technical SEO consultants providing technical SEO services and plentiful online resources to help you out.
If you install the correct schema markup plugins, understand how to use the Google Search Console, and develop a solid link-building strategy, you are well on your way to climbing those rankings and reaching your audience.
Ask The Content Strategist: FAQS About Technical SEO
What are the potential risks of relying solely on automated tools for technical SEO, and how can content marketers mitigate these risks?
Relying solely on automated tools for technical SEO may overlook nuanced issues that require manual intervention. Content marketers should supplement automated tools with manual audits and regular checks to ensure comprehensive optimization and mitigate the risk of overlooking critical issues.
How does user-generated content (UGC) impact technical SEO, and what strategies can content marketers employ to leverage UGC effectively for search visibility?
User-generated content can enrich websites with fresh and diverse content, potentially impacting technical SEO factors such as keyword density and content structure. Content marketers can encourage UGC through interactive features and community engagement, optimizing user-generated content for relevant keywords and ensuring proper technical implementation for search visibility.
What role does mobile optimization play in technical SEO, and how can content marketers ensure seamless user experiences across different devices?
Content marketers can ensure seamless user experiences across devices by implementing responsive design, optimizing page speed, and testing website performance on various mobile devices and screen sizes.
How do content distribution channels outside of search engines, such as social media platforms, impact technical SEO efforts, and what strategies can content marketers employ to maximize visibility across these channels?
Content distribution channels like social media platforms can indirectly impact technical SEO through increased brand visibility and referral traffic. Content marketers can maximize visibility across these channels by optimizing content for social sharing, engaging with relevant communities, and leveraging social media analytics to refine content distribution strategies for better search visibility.
Looking for more information on SEO best practices? Subscribe to The Content Strategist and follow us on Instagram.
Get better at your job right now.
Read our monthly newsletter to master content marketing. It’s made for marketers, creators, and everyone in between.